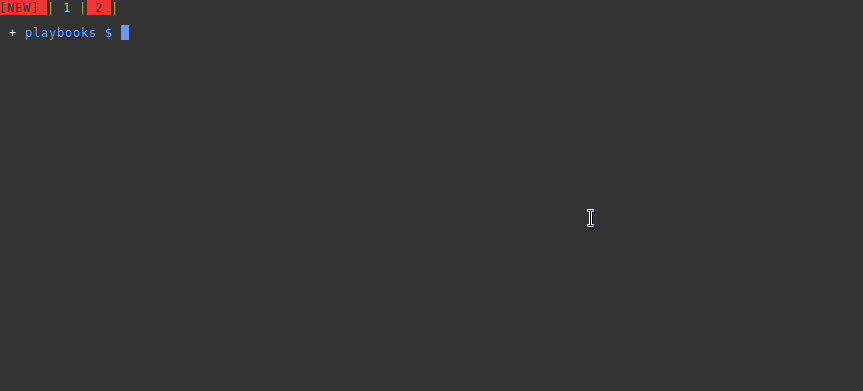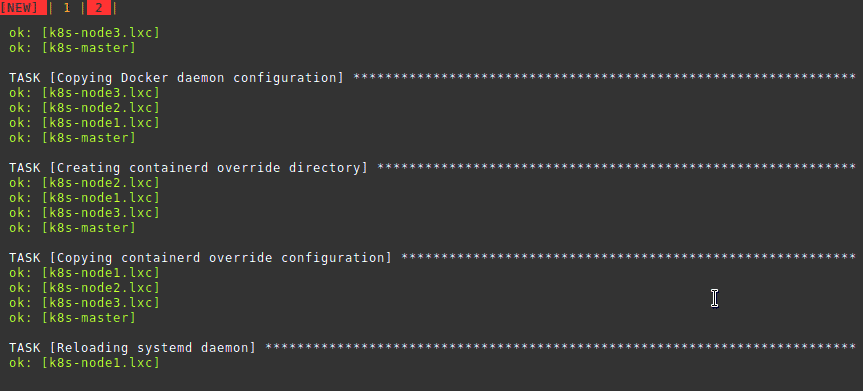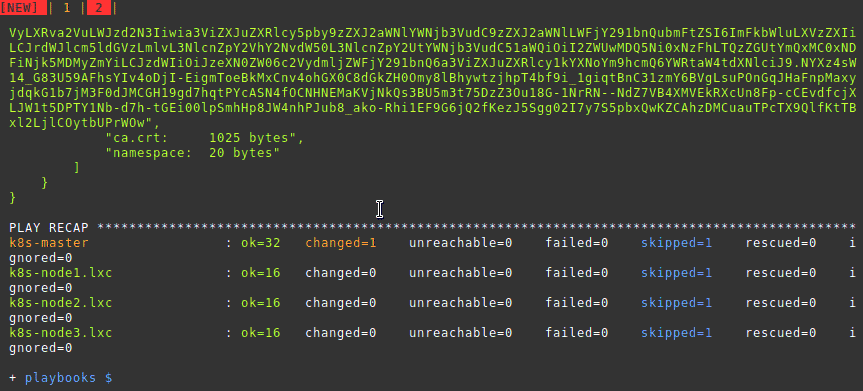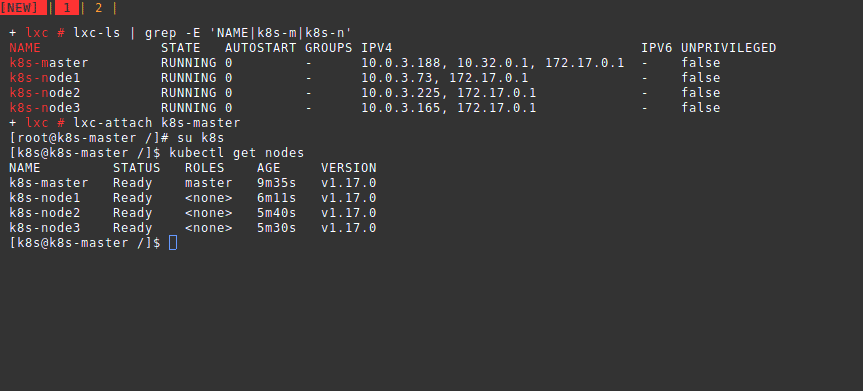Kubernetes in a Linux Container
Kubernetes is an open source container orchestration tool promising a catch all solution to issues that arise when deploying applications. Kubernetes creates a framework that models how infrastructure and services should interact.
The industry is trending in a direction where a
k8s (Kubernetes) setups in
one form or the other. Let’s exploit Linux Containers (LXC) as a mock
infrastructure and create a local k8s cluster to experiment.
The Base System
We will use CentOS Linux 8.1.1911 as our base system for a
cluster running k8s version 1.17. You can download the CentOS version of
choice using lxc-create.
shell
lxc-create -n k8s-centos8 -t downloadIn my case the rootfs for lxc is chroot, container, virtual machine,
and bare metal should be easy.
docker using a
Dockerfile. We
docker export
to obtain the container’s filesystem. This build bootstraps openssh-server and
python for ansible to quickly setup the clusters.
dockerfile
FROM centos:centos8.1.1911
RUN dnf -y update
RUN dnf install -y --setopt=install_weak_deps=False \
openssh-server network-scripts python3
RUN systemctl enable network
RUN systemctl disable kdump
RUN usermod -p "$(uuidgen)" root
COPY centos8/files/ifcfg-ens3 /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens3
COPY common/sshd_config /etc/ssh/sshd_config
RUN mkdir -p /root/.ssh
RUN chmod 700 /root/.ssh
COPY common/authorized_keys /root/.ssh/authorized_keys
RUN chmod 400 /root/.ssh/authorized_keysThe Container Configuration
For Kubernetes to work inside the container, we’ll need to tweak its lxc
configuration. This is a k8s-centos8 in /var/lib/lxc/k8s-centos8/config.
ini
# Uncomment the following line to support nesting containers
lxc.include = /usr/share/lxc/config/nesting.conf
# Distribution configuration
lxc.include = /usr/share/lxc/config/common.conf
lxc.arch = x86_64
# Allow access to all cgroups
lxc.cgroup.devices.allow = a
# Set proc mount to read and write
lxc.mount.auto = cgroup:mixed proc:rw sys:mixed
# No capability drops
lxc.cap.drop =
# Bind host kmsg for oom killer
lxc.mount.entry = /dev/kmsg dev/kmsg none defaults,bind,create=file
# Apparmor unconfined and allow nesting
lxc.apparmor.profile = unconfined
lxc.apparmor.allow_nesting = 1
# Network configuration
lxc.net.0.type = veth
lxc.net.0.link = lxcbr0
lxc.net.0.flags = up
lxc.net.0.hwaddr = 00:16:3e:e0:c3:1d
lxc.rootfs.path = dir:/var/lib/lxc/k8s-centos8/rootfs
lxc.uts.name = k8s-centos8Kubernetes Cluster Installation
The base system is now ready. -B overlayfs -s onto the end of the lxc-copy command for super fast
cloning.
/etc/default/lxc-net then you can ping a running container by
name.
shell
lxc-copy -n k8s-centos8 -N k8s-master
lxc-copy -n k8s-centos8 -N k8s-node1
lxc-copy -n k8s-centos8 -N k8s-node2
lxc-copy -n k8s-centos8 -N k8s-node3Manually setting up each system is troublesome. We automate the rest using
this
ansible