NixOps: Towards The Final Frontier
NixOps (Nix Operations) is a program for
deploying and provisioning multiple NixOS machines in a
network or cloud environment. This write up is by no means an
nixops
approach. You can also check out krops,
morph, and
deploy-rs as community alternatives to
nixops. You may also want to use the simpler
nixos-rebuild command.
shell
nixos-rebuild switch \
--target-host "nix@remote.host" \
--build-host "localhost" \
--no-build-nixBootstrapping Remote Machines
NixOps 2.0 supports
non-root deployments.
ssh access to the root user,
therefore you should bootstrap a remote machine using its configuration.nix.
Power users will use NixOS
generators
to
nix
{
services.openssh = {
enable = true;
permitRootLogin = "prohibit-password";
passwordAuthentication = false;
challengeResponseAuthentication = false;
extraConfig = "Compression no";
};
users.users.root = {
openssh.authorizedKeys.keyFiles = [ ./ssh-key.pub ];
};
}The user’s authorized_keys is users.users.<name?> where <name?> is the actual user.
users.users.<name?>.openssh.authorizedKeys.keyFiles. Do not use
users.users.<name?>.openssh.authorizedKeys.keys to configure public keys
as it replaces the authorized_keys that nixops sets on the remote machine.
Once nixops interfaces successfully with a remote machine it sets its public
key, as well as a private [pdf].
id_charon_vpn in the user’s .ssh folder. The
remote machines are now ready to accept connections from nixops.
Directory Structure
Let’s take a look at my directory nixops.
text
|__ configuration.nix
|__ deployments.nixops
|__ configuration
| |__ heron.nix
| |__ pigeon.nix
|__ hardware
| |__ heron.nix
| |__ pigeon.nix
|__ helpers
| |__ extra-builtins.nix
| |__ wrappers
| |__ vault
|__ keys
| |__ thedroneely.com.nix
|__ mailers
|__ packages
|__ programs
| |__ nix.nix
|__ servers
|__ users
| |__ pigeon.nix
| |__ root.nix
| |__ thedro.nix
|__ virtualizers
|__ websites
|__ thedroneely.com.nixThe deployment entry point is at configuration.nix. The machine specific
configuration.nix and hardware.nix are in the configuration and hardware
folders respectively. The deployment deployments.nixops.
This directory contains helpers, program specific configurations, as well as files responsible for secrets management. For example — this website is realized from an entry point that imports and implements every dependency it needs to function.
nix
{ config, lib, pkgs, ... }:
{
imports = [
../../keys/deployments/thedroneely.com.nix
../../servers/cgit/service.nix
../../servers/goaccess/service.nix
../../servers/isso/service.nix
../../servers/nginx/service.nix
../../servers/phpfpm/service.nix
../../servers/postgresql/service.nix
../../servers/rainloop/service.nix
];
}NixOps Deployment and Commands
Populate the configuration entry point configuration.nix with a list of
machines to provision in the deployment.
nix
{
network.description = "nixos";
network.enableRollback = true;
heron = {
imports = [ ./hardware/heron.nix ./configuration/heron.nix ];
deployment.targetHost = "heron.local";
};
talon = {
imports = [ ./hardware/talon.nix ./configuration/talon.nix ];
deployment.targetHost = "talon.local";
};
tiger = {
imports = [ ./hardware/tiger.nix ./configuration/tiger.nix ];
deployment.targetHost = "tiger.local";
};
hound = {
imports = [ ./hardware/hound.nix ./configuration/hound.nix ];
deployment.targetHost = "hound.local";
};
pigeon = {
imports = [ ./hardware/pigeon.nix ./configuration/pigeon.nix ];
deployment.targetHost = "pigeon.local";
};
}This entry point declares five machines to be operated on — each with their
own hardware and configuration specific assets under the network nixos.
Rollbacks are enabled for the nixops operator to switch generations in the
case of a mishap.
Make a deployment using create by referencing the entry point file path and
~/.nixops/deployments.nixops
--state.
shell
nixops create --deployment nixos --state deployments.nixops configuration.nixYou can also adjust the entry point file paths using modify. Below two files
configuration.nix and extra.nix are used as entry points.
shell
nixops modify --deployment nixos --state deployments.nixops configuration.nix extra.nixList all available nixops list depends on the last nixops deploy run.
list argument.
shell
$ nixops list --state deployments.nixops
+--------------------------------------+-------+-------------+------------+------+
| UUID | Name | Description | # Machines | Type |
+--------------------------------------+-------+-------------+------------+------+
| f56d276b-af54-11ea-b171-02422b1a33b6 | nixos | nixos | 5 | none |
+--------------------------------------+-------+-------------+------------+------+
nixops
deployment
nixos on all machines listed in
the entry point configuration using the deploy argument.
shell
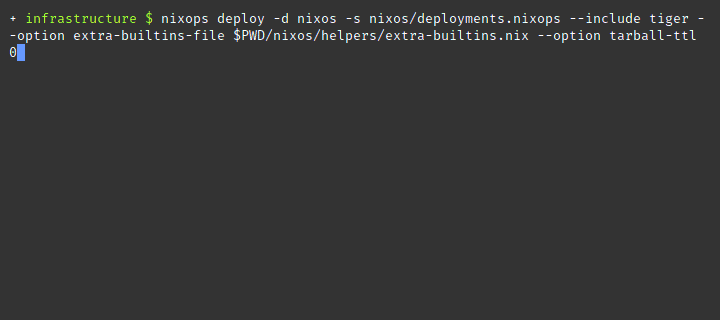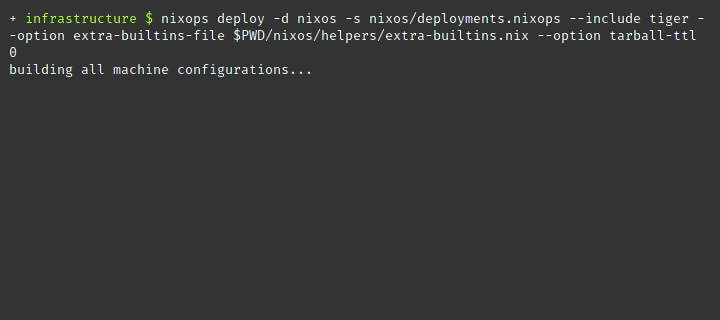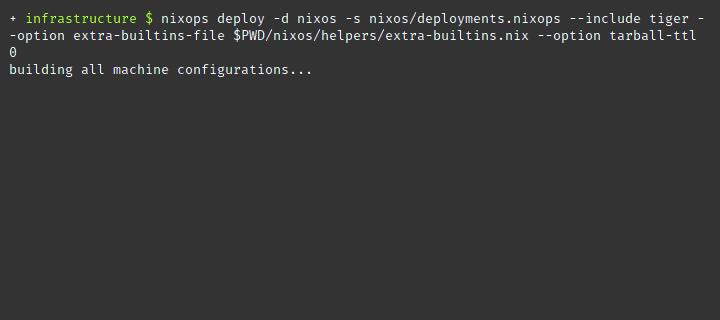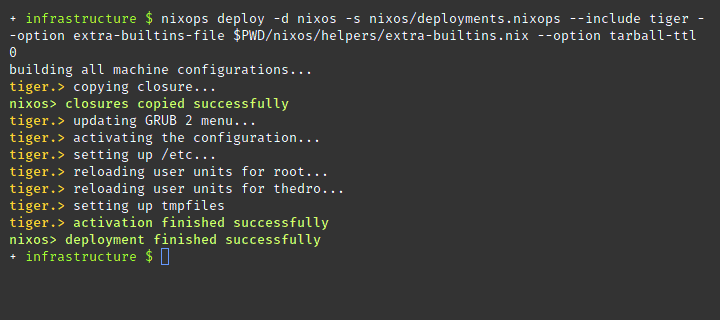
nixops deploy --deployment nixos --state deployments.nixopsRun the deployment nixos but only on the machine with the cryptonym heron
using --include.
shell
nixops deploy --deployment nixos --state deployments.nixops --include heronShow the state for deployment nixos using the info argument. This command
lists the status and current state of each machine.
shell
$ nixops info --deployment nixos --state deployments.nixops
Network name: nixos
Network UUID: f56d276b-af54-11ea-b171-02422b1a33b6
Network description: nixos
Nix expressions: /nixos/configuration.nix
Nix profile: /nix/var/nix/profiles/per-user/thedro/nixops/f56d276b-af54-11ea-b171-02422b1a33b6
+--------+-----------------+------+----------------------------------------------------+------------+
| Name | Status | Type | Resource Id | IP address |
+--------+-----------------+------+----------------------------------------------------+------------+
| heron | Up / Outdated | none | nixops-f56d276b-af54-11ea-b171-02422b1a33b6-heron | |
| hound | Up / Outdated | none | nixops-f56d276b-af54-11ea-b171-02422b1a33b6-hound | |
| pigeon | Up / Up-to-date | none | nixops-f56d276b-af54-11ea-b171-02422b1a33b6-pigeon | |
| talon | Up / Outdated | none | nixops-f56d276b-af54-11ea-b171-02422b1a33b6-talon | |
| tiger | Up / Up-to-date | none | nixops-f56d276b-af54-11ea-b171-02422b1a33b6-tiger | |
+--------+-----------------+------+----------------------------------------------------+------------+Examine the machines more closely with the check argument. This command
provides extra information such as load averages and failed units.
shell
$ nixops check --deployment nixos --state deployments.nixops --include tiger pigeon
Machines state:
+--------+--------+-----+-----------+----------+----------------+----------------------------------------+-------+
| Name | Exists | Up | Reachable | Disks OK | Load avg. | Units | Notes |
+--------+--------+-----+-----------+----------+----------------+----------------------------------------+-------+
| pigeon | Yes | Yes | Yes | N/A | 0.16 0.07 0.04 | proc-sys-fs-binfmt_misc.mount [failed] | |
| tiger | Yes | Yes | Yes | N/A | 0.11 0.09 0.03 | proc-sys-fs-binfmt_misc.mount [failed] | |
+--------+--------+-----+-----------+----------+----------------+----------------------------------------+-------+List the generations for deployment nixos. The deployment fleet is currently
on generation 203.
shell
$ nixops list-generations --deployment nixos --state deployments.nixops
200 2020-06-26 00:28:10
201 2020-06-26 04:14:40
202 2020-06-26 04:28:12
203 2020-06-26 21:58:55 (current)Rollback the deployment to a previous generation with the rollback argument.
Use --include to target specific machines.
shell
nixops rollback 201 --deployment nixos --state deployments.nixops --include heron ferretDelete a deployment with the delete argument but you must first remove the
machine resources with destroy.
shell
nixops destroy --deployment nixos --state deployments.nixops --include heron
nixops delete --deployment nixos --state deployments.nixopsNixOps Secrets Management
The nix store at /nix/store is world readable. Secrets entered directly into
any nix configuration will be available to all users on the system. Avoid
placing secrets into a nix configuration directly — as it will leak to
unprivileged users. NixOps provides a powerful secrets management system in the
form of password files.
Using a password file provides indirection and guards against writing secrets
directly into your nix files. NixOps writes deployment keys to /run/keys.
Users must be a part of the key
group
to access deployment keys on the system.
NixOps can set the permissions, owners, and groups of each key. In my case, the
builtins.extraBuiltins. This
blog post
gives an excellent rundown on this technique, and
this wiki
compares the different secret management approaches. A sample of the nix
secrets configuration for this website is shown
nix
{ config, ... }:
let user = "thedroneely"; in
{
deployment.keys = {
thedroneely_cockpit_api_token = {
user = user;
text = "${builtins.extraBuiltins.vault "thedroneely/thedroneely.com" "cockpit_api_token"}";
};
thedroneely_pgsql_database_password = {
user = user; group = "postgres"; permissions = "0640";
text = "${builtins.extraBuiltins.vault "thedroneely/thedroneely.com" "pgsql_database_password"}";
};
thedroneely_ssh_known_hosts = {
inherit user;
text = "${builtins.extraBuiltins.vault "thedroneely/thedroneely.com" "ssh_known_hosts"}";
};
};
}Enable extraBuiltins by linking directly to the nix-plugins package on the
nix operator host. Allow users in @wheel to become trusted users and wield
this ultimate power.
nix
{ pkgs, config, ... }:
{
nix.extraOptions = ''
trusted-users = root @wheel
plugin-files = ${pkgs.nix-plugins}/lib/nix/plugins/libnix-extra-builtins.so
'';
}Create helpers/extra-builtins.nix and extend the builtins with custom
functions. The vault function below accepts a field and a path as
arguments to an external wrapper.
nix
{ exec, ... }:
{
vault = path: field: exec [ ./wrappers/vault field path ];
}The wrapper returns the secret result from vault as a string. NixOps is now
aware of keys available from a vault server. This is done at evaluation time.
Environment variables are available to wrappers called from extraBuiltins.
shell
#!/bin/sh -eu
printf '"' && vault kv get -field "$1" "$2" && printf '"'Load the extraBuiltins with any nixops command by
nix.conf.
--option flag
with the file path. Vault keys are called using builtins.extraBuiltins.vault.
shell
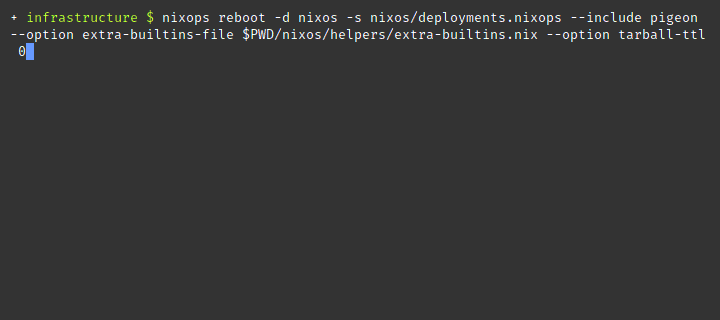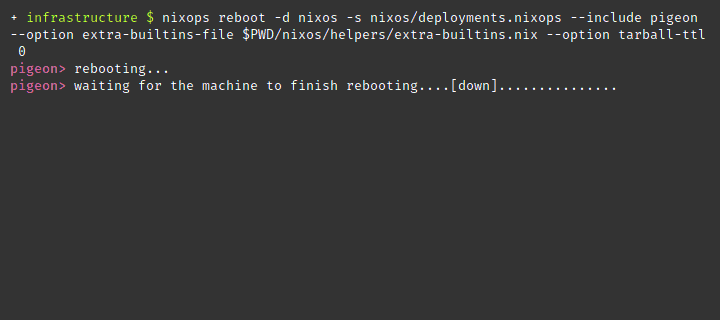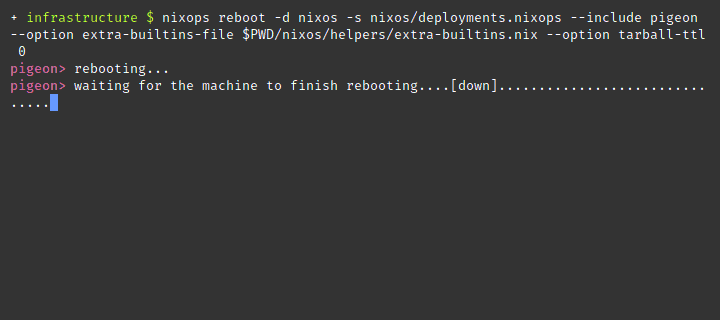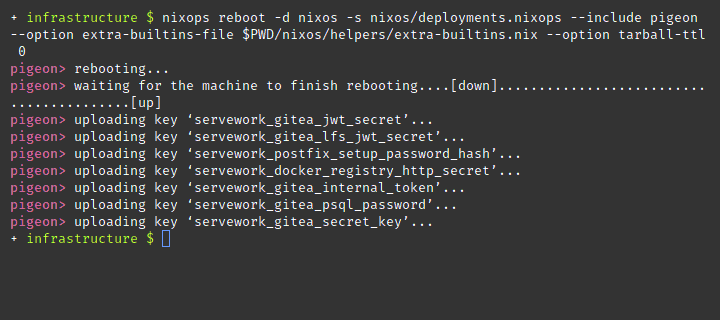
nixops reboot --deployment nixos --state deployments.nixops --include pigeon --option extra-builtins-file $PWD/nixos/helpers/extra-builtins.nixThe keys in /run/keys are ephemeral and never touch storage. Do
nixops on the
same nixops host won’t end well if secrets are set.
nixops. Your keys will be lost and any
dependent service will nixops to remotely reboot a machine and its keys will be seeded back into
position. Wonderful.
Upload deployment keys immediately without waiting on a deploy by using the
send-keys argument.
shell
nixops send-keys --deployment nixos --state deployments.nixops --include pigeonNixOps Pinning
NixOps depends on the nix channel set on the host. This is a very interesting
nixops on a machine with an
uncertain channel is an assured gotcha.
nix shell
until more of the code is read.
NIX_PATH
to your nixops commands.
shell
NIX_PATH=nixpkgs=https://github.com/NixOS/nixpkgs/archive/2b417708c282d84316366f4125b00b29c49df10f.tar.gzCheck the system’s channel version by running nixos-version or
nix-instantiate if you prefer to use nix-channel directly.
shell
nix-instantiate --eval --expr '(import <nixpkgs> {}).lib.version'NixOps and Nix Channel
Syncing the channel on the host and remote with nix-channel works out
nix-env or nix-shell environments.
nix flake
(manual)
to completely replace the channel mechanism. The channel list is at
releases.nixos.org and status at
status.nixos.org. In my case, a “lock” file called
versions.nix is created containing all sources of truth.
nix
{
# Channel Status: https://status.nixos.org
# Channel List: https://releases.nixos.org/?prefix=nixos
pkgs = import <nixpkgs> { };
"20.03" = { channel = "https://releases.nixos.org/nixos/20.03/nixos-20.03.3061.360e2af4f87"; };
"20.09" = { channel = "https://releases.nixos.org/nixos/20.09/nixos-20.09.2468.c6b23ba64ae"; };
"21.05" = { channel = "https://releases.nixos.org/nixos/21.05/nixos-21.05.1486.2a96414d7e3"; };
"21.11" = { channel = "https://releases.nixos.org/nixos/21.11/nixos-21.11.336020.2128d0aa28e"; };
"22.05" = { channel = "https://releases.nixos.org/nixos/22.05/nixos-22.05.998.d17a56d90ec"; };
unstable = import (builtins.fetchTarball {
url = "https://releases.nixos.org/nixos/unstable/nixos-22.11pre386147.e0a42267f73/nixexprs.tar.xz";
sha256 = "0y6q1j17lmhxh1pqi2jj6xr21pnmachra48336nnbcpnxizswjgg"; }) { };
linux_5_6_10 = import (builtins.fetchTarball {
url= "https://github.com/NixOS/nixpkgs/archive/b0e3df2f8437767667bd041bb336e9d62a97ee81.tar.gz";
sha256 = "0d34k96l0gzsdpv14vnxdfslgk66gb0nsjz7qcqz1ykb0i7n3n07"; }) { };
linux_5_7_7 = import (builtins.fetchTarball {
url= "https://github.com/NixOS/nixpkgs/archive/f761c14fd2f198f64cc5483ebf9f83222f9214aa.tar.gz";
sha256 = "09w0n8qvldanab1m6ik507nl48aszam2a5ii3z2fvk72s66zmry7"; }) { };
linux_5_10_13 = import (builtins.fetchTarball {
url= "https://github.com/NixOS/nixpkgs/archive/75d4d5fe851a.tar.gz";
sha256 = "0ks99va26jsq1mdr1mk9p9r75zvj6ghlmqkdcf4yak0dwr7j48a6"; }) { };
}A systemd service is created using restartTriggers to lazily watch
versions.nix for attribute changes. The system will sync up as
nixos-rebuild if nixops is not available or fails.
nix
{ config, pkgs, ... }:
let channel = (import ../versions.nix)."${config.system.stateVersion}".channel; in
{
systemd.services.nix-channel-update = {
description = "Update Nix Channels";
wantedBy = [ "multi-user.target" ];
after = [ "network.target" ];
restartTriggers = [ channel ];
path = [ pkgs.shellcheck pkgs.nix ];
script = ''
set -euxo pipefail
shellcheck "$0" || exit 1
nix-channel --add "${channel}" nixos
nix-channel --update
'';
serviceConfig = { RemainAfterExit = "yes"; };
};
}The option config.system.stateVersion is the system’s canonical state version
— query the current and default value with the command
nixos-option system.stateVersion.