NixOS in The Wild
Nix and NixOS are two technologies that my
eyes have been on for a few years. Nix is the independent package manager that
allows for 99% reproducible.
shell
14:39:28 up 502 days, 15:30, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05Let’s discuss the 20.03 commits.
The Package Repository
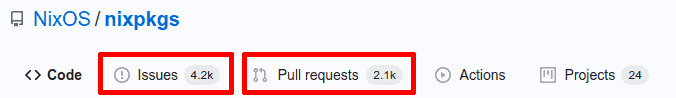
The nix Package Repository or nixpkgs
contains every package derivation. My one pain point is that
GitHub chokes on this repository hard.
Searching the right term over 4,000+ issues can intermittently
site queries.
text
site:https://github.com/NixOS/nixpkgs/issues <keyword>Online Documentation and Search Discovery
In my experience, the online documentation has poor search discoverability.
Nix’s HTML page. These pages are impeccable under the hood
with anchor id links on each section and subsection, but search
 Searching
for phases on Bing
Searching
for phases on Bing
id fragments on the search engine
results page (SERP). Most search queries send you to the top of the
nix package manual.
Local Documentation and Troubleshooting
NixOS provides a lot of documentation out of the box that is specific to every
installation. Users familiar with man will run man configuration.nix to see
nixos-option if you know
what you are looking for.
configuration.nix documentation is more accurate than searching
the online NixOS options index.
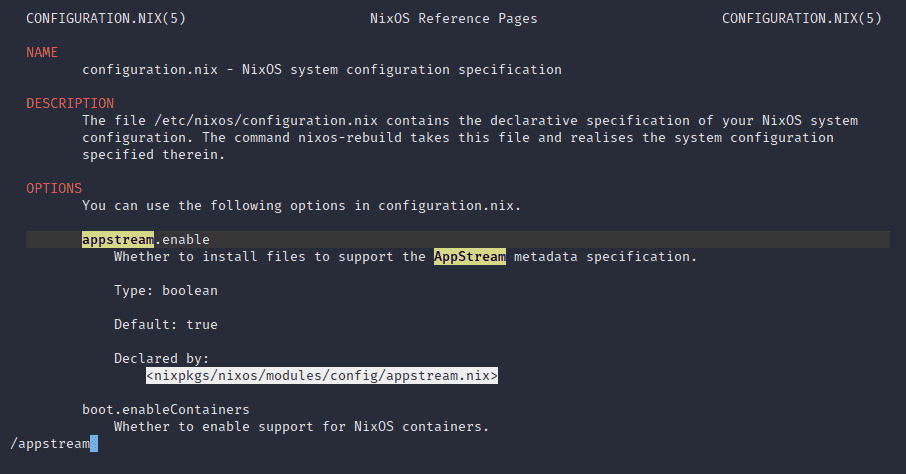
In fact, the entire package repository
(nixpkgs) resides on every installation as a channel. In the above manpage
nixpkgs/nixos/modules/config/appstream.nix declares the logic behind
appstream.enable. View this file by listing the channel name as root and
navigating to the per user channel source tree.
shell
$ sudo nix-channel --list
nixos https://releases.nixos.org/nixos/20.03/nixos-20.03.2351.f8248ab6d9e
$ tree -L 1 /nix/var/nix/profiles/per-user/root/channels/nixos
|__ COPYING
|__ default.nix
|__ doc
|__ flake.nix
|__ lib
|__ maintainers
|__ nixos
|__ nixpkgs -> .
|__ pkgs
|__ programs.sqlite
|__ README.md
|__ svn-revision
$ nix-instantiate --eval -E '(import <nixpkgs> {}).lib.version'
"20.03.2351.f8248ab6d9e"This is good to know even if you don’t care about the source purely as a reminder that not every system has the same state or exposes the same configuration options.
User Autologin
Most of my desktop machines do not use login managers. The auto login settings
of NixOS are login manager dependent. Apparently it’s trivial to override the
autovt@tty1 service and force auto login for any user without having to
install a login manager. Set restartIfChanged to false to avoid restarting
your desktop.
nix
{ pkgs, ... }:
{
systemd.services."autovt@tty1" = {
after = [ "systemd-logind.service" ];
restartIfChanged = false;
serviceConfig = {
Type = "simple";
ExecStart = "${pkgs.utillinux}/sbin/agetty --autologin ${username} --noclear %I $TERM";
Restart = "always";
};
};
}The above will not work in
future versions,
as it is simplified to the option services.getty.autologinUser. Be careful
though, enabling this option auto logs into every getty and the first activation
restarts the currently running session.
nix
{
services.getty.autologinUser = "username";
}Updating NixOS
Updating NixOS is tricky business. The short of it is that generally the system
wide channel is the repository used to source updates. Most systems have one
channel called nixos or nixpkgs under the user root. Every user inherits
the root user’s channel unless they have set their own per user channel.
- Using
rootlist the channel withnix-channel --list - Override or add a channel with
nix-channel --add - Update the channel with
nix-channel --update - Upgrade every per user environment with
nix-env --upgrade That’s rather cumbersome manually (but for good reason). My preference is to sync the channel declaratively with nixopsand use a per user declarative configuration withnix-env.nixos-rebuild switch --upgrade
shell
# nix-channel --list
nixos https://nixos.org/channels/nixos-20.03
# nix-channel --add 'https://nixos.org/channels/nixos-20.03' nixos
# nix-channel --update
# nix-env --upgrade
# nixos-rebuild switch --upgradeIf you trust the stability, you can use system.autoUpgrade.enable and
system.autoUpgrade.channel, but those are scary options for my use case.
Shellcheck and systemd
Every language, system, or framework leads you down a certain path. NixOS coaxes
you down the path of writing lots of shell scripts with systemd. Save
yourself the pain — set the shell to a stricter mode and run
shellcheck upon service execution.
nix
{ pkgs, ... }:
{
systemd.services.my-service = {
description = "My service";
wantedBy = [ "multi-user.target" ];
path = [ pkgs.shellcheck ];
script = ''
set -euxo pipefail
shellcheck "$0" || exit 1
# Code goes here...
'';
};
}LibreOffice and Spell Checking
Spell checking is a commonly used feature of
LibreOffice. On my NixOS 20.03 machines,
LibreOffice spell checking doesn’t seem to work. Add the missing dictionary
package links and expose them using DICPATH. Log out and back in and
LibreOffice should find the spell checking modules.
nix
{ pkgs, ... }:
{
environment.systemPackages = with pkgs; [
hunspell
hunspellDicts.en_US-large
hyphen
];
environment.pathsToLink = [ "/share/hunspell" "/share/myspell" "/share/hyphen" ];
environment.variables.DICPATH = "/run/current-system/sw/share/hunspell:/run/current-system/sw/share/hyphen";
}Hashless Git Fetching
Use the function builtins.fetchGit to fetch the HEAD of a repository branch
directly without stipulating a hash. The builtin function fetchGit will fetch
any git repository at evaluation time — allowing for automation, ssh-agent
integration, and other niceties.
nix
{ stdenv }:
let url = "https://github.com/koalaman/shellcheck"; in
stdenv.mkDerivation rec {
pname = "shellcheck";
version = "master";
src = builtins.fetchGit { inherit url; ref = "refs/heads/master"; };
dontBuild = true;
installPhase = ''
runHook preInstall
mkdir $out
# Code goes here...
runHook postInstall
'';
}Package Tracking and systemd
In a continuous integration and deployment (CI/CD) environment you can set a
systemd service to restart on package changes. Use restartTriggers to track
upstream package definitions.
nix
{ pkgs, ... }:
let package = pkgs.callPackage ./default.nix {}; in
{
systemd.services.my-service = {
description = "My service";
wantedBy = [ "multi-user.target" ];
restartTriggers = [ package ];
path = [ pkgs.shellcheck ];
script = ''
set -euxo pipefail
shellcheck "$0" || exit 1
# Code goes here...
'';
serviceConfig = { RemainAfterExit = "yes"; };
};
}Internet Connectivity in the Nix Sandbox
Nix build environments prohibit internet connections outside the scope of
defined functions like fetchgit or fetchurl. You can remove this restriction
by setting the correct expected hash recursively before evaluation. This allows
us to do “illegal” things like the following.
nix
{ stdenv, pkgs }:
let url = "https://thedroneely.com/git/thedroneely/thedroneely.com.git"; in
stdenv.mkDerivation rec {
pname = "composer";
version = "master";
src = builtins.fetchGit { inherit url; ref = "refs/heads/master"; };
buildInputs = [ pkgs.cacert pkgs.php74Packages.composer ];
dontBuild = true;
installPhase = ''
runHook preInstall
composer --no-cache install
mkdir $out
cp -r vendor $out/vendor
runHook postInstall
'';
outputHashAlgo = "sha256";
outputHashMode = "recursive";
outputHash = "0zkqkbwz5vg4k95s83pl0kxvphav1wzmivs5b1kmwf101wnj1m4q";
}Check out this neat blog for more interesting approaches and tips of this nature.
Kernel Patching for Kids
Applying kernel patches using fetchurl in NixOS is a trivial endeavour. You
should manually patch, configure, and compile a kernel at least once to
understand what’s happening.
nix
{
boot.kernelPatches = [
{ name = "ck-5.6"; patch = (builtins.fetchurl {
url = "http://ck.kolivas.org/patches/5.0/5.6/5.6-ck2/patch-5.6-ck2.xz";
sha256 = "18rk9023b14x62n0ckbnms6ahq5yjramz7qfjagkaga95i8ha6b2"; });
}
{ name = "uksm-5.6"; patch = (builtins.fetchurl {
url= "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dolohow/uksm/master/v5.x/uksm-5.6.patch";
sha256 = "021sylwacamh8q26agcp0nmmw3ral2wl7bgibmi379irnvy0c37y"; });
}
{ name = "userns-overlayfs"; patch = (builtins.fetchurl {
url= "https://kernel.ubuntu.com/git/ubuntu/ubuntu-xenial.git/patch/?id=0c29f9eb00d76a0a99804d97b9e6aba5d0bf19b3";
sha256 = "1j4ind31hgkjazbgfd64lpaiqps8hcsqkar4v6nvxrpysmkg9nfd"; });
}
];
}Nginx and its Temporary Folders
The permissions and ownership on nginx’s
temporary folders can change in peculiar circumstances. There is a chance that
the user nginx becomes dissociated from its folders when disabling and
re-enabling nginx using the option services.nginx.enable. The temp folders
for nginx are in /var/spool/nginx on system version 20.03. Use systemd’s
tmpfiles.d to ensure that these permissions always stay consistent. This is
solved in version 20.09.
nix
{
systemd.tmpfiles.rules = [
"z /var/spool/nginx 0700 nginx nginx -"
"z /var/spool/nginx/client_body_temp 0700 nginx nginx -"
"z /var/spool/nginx/fastcgi_temp 0700 nginx nginx -"
"z /var/spool/nginx/logs 0700 nginx nginx -"
"z /var/spool/nginx/proxy_temp 0700 nginx nginx -"
"z /var/spool/nginx/scgi_temp 0700 nginx nginx -"
"z /var/spool/nginx/uwsgi_temp 0700 nginx nginx -"
];
}The Hash as Truth
A common mode of failure when working with Nix and NixOS is that
nix knows the hashes of already built resources.
If you want to set a new sha256 and force a rebuild: don’t place a random
dummy string or change one of the characters in the original sha256. Always
use lib.fakeSha256 or the command nix-prefetch-url to fetch the new sha256
hash.
The reason is simple — if you happen to use an already known hash, then nix
may download the correlated binaries from a cached location and leave you with
an interesting debugging session. The sha256 attributes always take precedence
— changing only the pname or version attributes in most cases will have no
effect.
nix
{ lib, stdenv, fetchurl }:
stdenv.mkDerivation rec {
pname = "puppeteer-docs";
version = "latest";
src = fetchurl {
url = "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/puppeteer/puppeteer/main/docs/api.md";
sha256 = lib.fakeSha256;
};
phases = [ "installPhase" ];
installPhase = ''
runHook preInstall
mkdir -p $out
cp ${src} $out/api.md
runHook postInstall
'';
meta = with lib; {
description = "Puppeteer Documentation";
homepage = "https://github.com/puppeteer/puppeteer/blob/main/docs/api.md";
};
}Nix Commands and Local Caching
Nix is slow and caches to improve speed. Local caching can sometimes interfere
with automation tasks when using commands like nix-build or nixops. Use the
--option argument and set the tarball-ttl to 0 to ensure you are always
pulling fresh sources and repositories.
shell
$ nixops deploy -d deployment --option tarball-ttl 0
$ nix-build --option tarball-ttl 0If you are running a lean system, make the
time to live (TTL) settings
permanent with nix.extraOptions in the system configuration.
nix
{
nix.extraOptions = ''
tarball-ttl = 0
narinfo-cache-negative-ttl = 0
narinfo-cache-positive-ttl = 0
'';
}Logs and Logrotate
On NixOS, it’s systemd
journald.
The defaults are okay, but logrotate is a crucial program in my stack.
The abstraction for logrotate is fine, and it’s trivial to mimic my preferred
setup as it would be on any traditional Linux distribution. Enable logrotate
with a default preset.
nix
{
services.logrotate = {
enable = true;
config = ''
compress
create
daily
dateext
delaycompress
missingok
notifempty
rotate 31
'';
};
}Create a per service setup using the config
config attribute is of type
types.lines which basically means it will mix down or append all declarations
into a single logrotate.conf.
nginx).
nix
{
services.logrotate.config = ''
/var/spool/nginx/logs/*.log {
create 644 nginx nginx
postrotate
systemctl reload nginx
endscript
}
'';
}Using the Force
Breaking the assumptions of abstractions and frameworks is a hobby of mine.
Sometimes there are special situations where the abstractions get in the way of
the desired configuration. Use lib.mkForce as a forcing action to
mkForce is
an alias of
mkOverride 50 which sets the override priority of a configuration
option.
/etc/nsswitch.conf using environment.etc and
lib.mkForce to prevent casualties.
nix
{ lib, ... }:
{
environment.etc."nsswitch.conf".text = lib.mkForce ''
rpc: files
shadow: files
ethers: files
networks: files
services: files
netgroup: files
publickey: files
protocols: files
group: files systemd
passwd: files systemd
hosts: files mymachines myhostname libvirt libvirt_guest mdns4_minimal resolve [!UNAVAIL=return] dns
'';
}